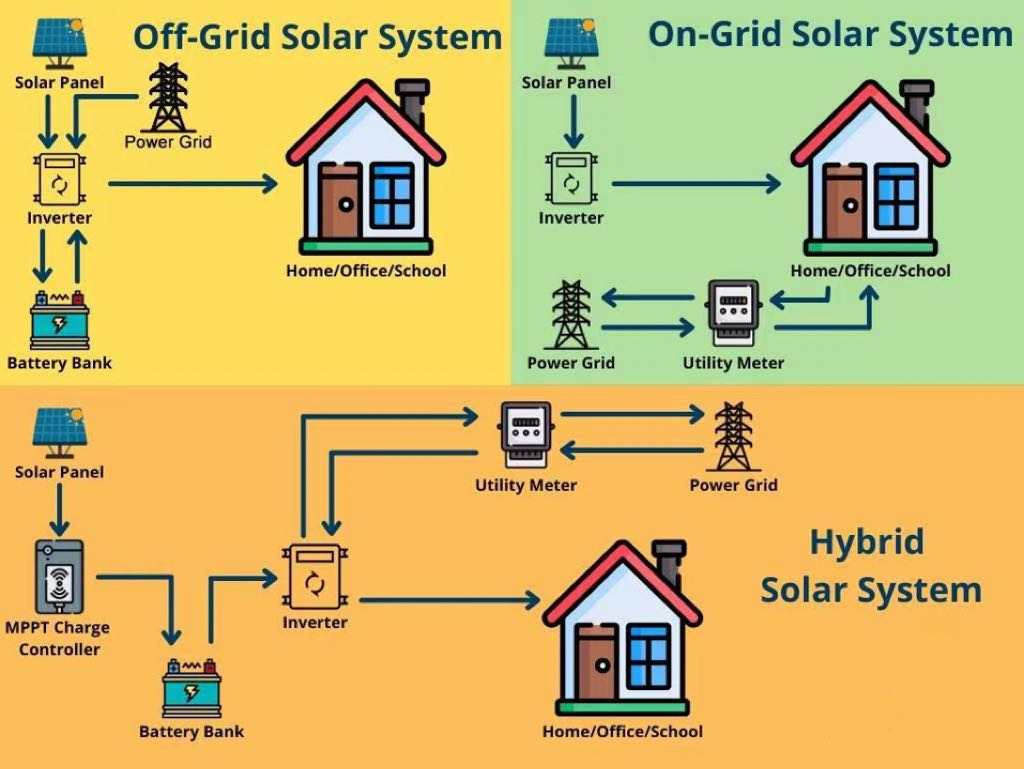
# What is the difference between off-grid inverter and grid-connected inverter? #
Off-grid inverters and grid-connected inverters are the two main types of inverters in solar systems. Their functions and application scenarios are significantly different:
Off-grid Inverter
Off-grid inverters are used in solar systems that are not connected to a traditional grid. They are often used in conjunction with battery storage systems to store excess electricity generated by solar panels.
Main function: Convert direct current (DC) generated by solar panels or other renewable energy devices into alternating current (AC) for use in homes or devices.
Battery charging: It has the ability to manage battery charging, control the charging and discharging process of the battery, and protect the battery life.
Independent operation: does not rely on the external power grid and can operate independently when the power grid is unavailable. It is suitable for remote areas or places with unstable power grids.
Grid-tie Inverter
Grid tie inverters are used in solar systems connected to the public grid. This inverter is designed to maximize the conversion of solar energy into electricity and feed it into the grid.
Main function: Convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that meets grid standards and feed it directly into the home or commercial power grid.
No battery storage: Typically not used with battery systems as their main purpose is to deliver power directly to the grid.
Energy feedback: Excess electricity can be sold back to the grid, and users can reduce electricity bills through feed meters (Net Metering).
Key differences
Grid dependency: Off-grid inverters operate completely independent of the grid, while grid-tied inverters require a connection to the grid.
Storage capacity: Off-grid systems usually require batteries to store energy to ensure continuous power supply; grid-connected systems send the generated energy directly to the grid and do not require battery storage.
Safety features: Grid-connected inverters have necessary safety functions, such as anti-island protection (preventing continued power transmission to the grid when the grid is out of power), ensuring the safety of maintenance grid and workers.
Application scenarios: Off-grid systems are suitable for areas with no access to the power grid or poor grid service quality; grid-connected systems are suitable for cities or suburbs with stable power grid services.
Which type of inverter is chosen depends on the user’s specific needs, geographical location, and need for power system independence.
# On/Off grid solar inverter#
Post time: May-21-2024